Making of the fittest natural selection and adaptation answers – Making the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation is a fascinating topic that delves into the intricate processes that shape the evolution of life on Earth. This topic explores the fundamental principles of natural selection and adaptation, revealing how organisms have evolved to thrive in diverse environments.
Natural selection, the driving force behind the survival of the fittest, has played a pivotal role in shaping the diversity of life forms. This concept, coupled with adaptation, the remarkable ability of species to adjust to their surroundings, provides a comprehensive understanding of the evolutionary journey.
Making of the Fittest: Natural Selection
Natural selection is a driving force in evolution, favoring the survival and reproduction of individuals with traits that enhance their adaptation to their environment. Over time, this process leads to the accumulation of advantageous traits within a population, increasing the overall fitness of the species.
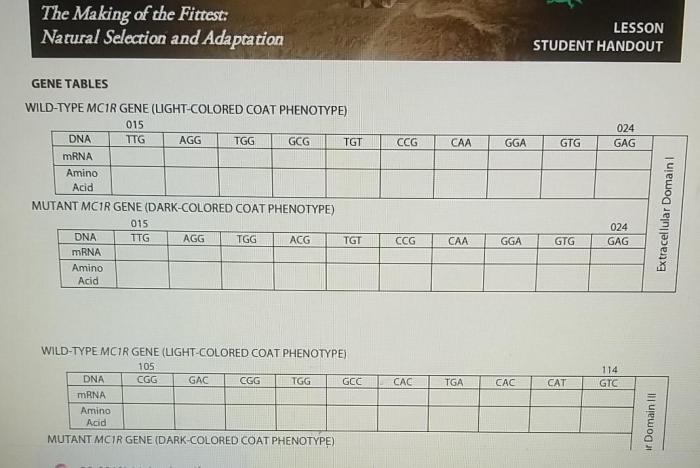
Natural selection operates through three key mechanisms: variation, selection, and inheritance. Genetic variation within a population provides the raw material for natural selection to work upon. Environmental pressures, such as competition for resources or predation, act as selective forces, favoring individuals with traits that increase their chances of survival and reproduction.
The traits that contribute to fitness are then passed on to offspring through inheritance, ensuring their continued presence in the population.
Examples of Natural Selection, Making of the fittest natural selection and adaptation answers
- Peppered moths: During the Industrial Revolution, soot from factories darkened tree trunks, providing camouflage for dark-colored moths. As a result, dark-colored moths became more prevalent than light-colored moths, demonstrating the power of natural selection in response to environmental change.
- Antibiotic resistance in bacteria: Bacteria that acquire mutations conferring resistance to antibiotics have a survival advantage over non-resistant bacteria. Over time, this leads to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, highlighting the role of natural selection in the spread of resistance.
Adaptation: Response to Environmental Pressures: Making Of The Fittest Natural Selection And Adaptation Answers
Adaptation refers to the traits or characteristics of an organism that enhance its survival and reproductive success in a specific environment. Adaptations arise through natural selection, favoring individuals with traits that provide an advantage in their particular ecological niche.
Examples of Adaptations
- Camouflage: Many animals have evolved camouflage to avoid predators or attract prey. For example, stick insects resemble twigs, while chameleons can change their skin color to match their surroundings.
- Migration: Birds and other animals migrate to regions with more favorable conditions during certain seasons. This adaptation allows them to escape harsh weather or find food sources.
Coevolution: Interdependent Adaptations

Coevolution describes the reciprocal evolutionary changes that occur between two or more species that interact closely. One species’ adaptation can drive the evolution of adaptations in the other species, leading to a dynamic and interdependent relationship.
Examples of Coevolutionary Relationships
- Predator-prey relationships: Predators evolve traits that enhance their ability to capture prey, while prey evolve defenses to avoid predation. This ongoing evolutionary arms race has shaped the adaptations of many species.
- Plant-pollinator relationships: Plants evolve flowers that attract specific pollinators, while pollinators evolve mouthparts and behaviors that allow them to access nectar and pollen.
Extinction and Speciation: Evolutionary Outcomes
Extinction is the irreversible loss of a species from Earth, while speciation is the formation of a new species from an existing one. Both processes are essential components of the evolutionary process.
Examples of Extinction Events and Speciation Events
- Extinction events: The Permian-Triassic extinction event wiped out over 90% of marine species, creating opportunities for new species to evolve and diversify.
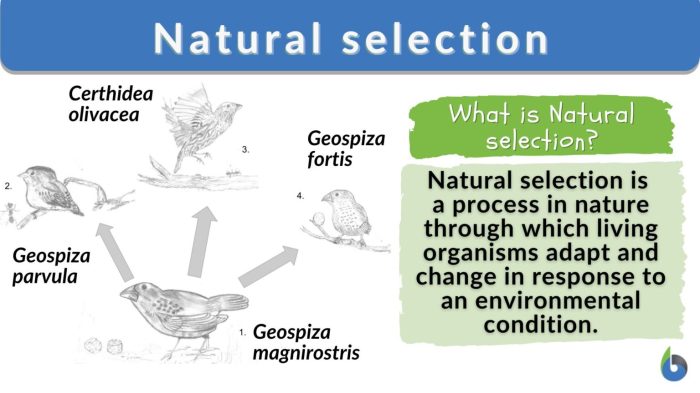
- Speciation events: The Galapagos finches evolved from a single ancestral species into multiple distinct species with beaks adapted to different food sources.
Quick FAQs
What is the role of genetic variation in natural selection?
Genetic variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon. It introduces diversity into a population, allowing for individuals with advantageous traits to survive and pass on their genes.
How do adaptations arise?
Adaptations can arise through various mechanisms, including genetic mutations, genetic recombination, and natural selection. These processes introduce new traits into a population, which can then be selected for or against based on their impact on survival and reproduction.