In the final stages of production a pharmaceutical is sterilized – In the final stages of production, pharmaceutical sterilization plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. This process eliminates microorganisms that can contaminate and compromise the quality of the drug, safeguarding patient health and well-being.
Sterilization techniques vary depending on the product and its intended use, with each method offering unique advantages and disadvantages. Validation studies are crucial to verify the effectiveness of sterilization processes, while quality control measures guarantee the sterility of the final product.
Introduction
Pharmaceutical production involves a series of complex processes, with sterilization playing a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of the final product. Sterilization eliminates microorganisms that can contaminate pharmaceuticals, preventing their proliferation and potential harm to patients.
Sterilization Methods

Various sterilization methods are employed in pharmaceutical production, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Heat Sterilization:Effective against most microorganisms, achieved through dry heat or moist heat (autoclaving).
- Radiation Sterilization:Utilizes gamma radiation or electron beam radiation to penetrate and kill microorganisms.
- Filtration Sterilization:Removes microorganisms by passing the product through a filter with a pore size smaller than the target organisms.
- Chemical Sterilization:Involves the use of chemical agents like ethylene oxide or hydrogen peroxide to kill microorganisms.
Validation of Sterilization, In the final stages of production a pharmaceutical is sterilized
Validating sterilization processes is essential to ensure their effectiveness and consistency. Validation methods include:
- Biological Indicators:Using microorganisms known to be highly resistant to sterilization to verify the efficacy of the process.
- Physical Indicators:Measuring physical parameters like temperature or pressure during sterilization to ensure they meet predefined criteria.
- Chemical Indicators:Utilizing chemical reactions that change color or fluorescence in response to specific sterilization conditions.
Quality Control
Stringent quality control measures are implemented to ensure the sterility of pharmaceutical products:
- Testing:Conducting microbiological tests on samples to detect any microbial contamination.
- Inspection:Visually examining packaging and equipment for any defects or breaches that could compromise sterility.
- Environmental Monitoring:Regularly monitoring the production environment to detect potential sources of contamination.
Regulatory Considerations: In The Final Stages Of Production A Pharmaceutical Is Sterilized

Pharmaceutical sterilization is subject to strict regulatory requirements:
- FDA (United States):Enforces the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for pharmaceutical sterilization.
- EMA (European Union):Issues guidelines on pharmaceutical sterilization in the European Pharmacopoeia.
- WHO (World Health Organization):Provides global guidance on pharmaceutical sterilization through its Technical Report Series.
Case Studies
Successful sterilization processes in pharmaceutical production:
- Sterilization of Injectables:Autoclaving vials and ampoules containing liquid formulations to ensure sterility.
- Radiation Sterilization of Medical Devices:Gamma radiation used to sterilize implantable devices and other medical equipment.
- Filtration Sterilization of Biologics:Ultrafiltration membranes employed to remove viruses and bacteria from biological products.
Emerging Trends
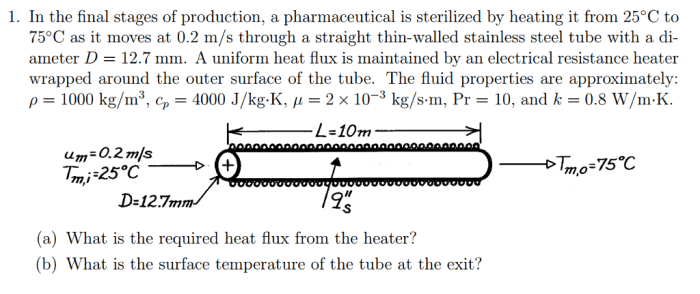
Advancements in sterilization technology:
- Non-thermal Sterilization:Exploring alternative methods like pulsed electric fields and high-pressure processing to minimize heat damage.
- Continuous Sterilization:Developing automated and continuous sterilization processes for increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Sterilization Verification Technologies:Utilizing sensors and real-time monitoring systems to enhance the accuracy and reliability of sterilization validation.
User Queries
Why is sterilization essential in pharmaceutical production?
Sterilization eliminates microorganisms that can contaminate and compromise the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
What are the different sterilization methods used in the industry?
Common sterilization methods include heat sterilization, radiation sterilization, and filtration.
How is the effectiveness of sterilization processes validated?
Validation studies are conducted to verify the ability of a sterilization process to eliminate microorganisms effectively.
What quality control measures are implemented to ensure sterility?
Quality control measures include testing, inspection, and environmental monitoring to maintain sterility throughout the production process.
How do regulatory considerations impact pharmaceutical sterilization?
Regulatory agencies establish guidelines and standards to ensure the safety and efficacy of sterilized pharmaceutical products.