The amount of energy produced by power-generating dams is a critical factor in the global energy landscape, providing a significant portion of the world’s electricity. This article delves into the intricate details of dam energy production, exploring its capacity, efficiency, environmental impact, economic considerations, and future trends.
Power-generating dams harness the energy of flowing water to generate electricity, playing a vital role in meeting the growing energy demands of modern society. Understanding the factors that influence their energy production capacity, such as dam size, water flow, and technological advancements, is essential for optimizing their performance.
Energy Generation Capacity
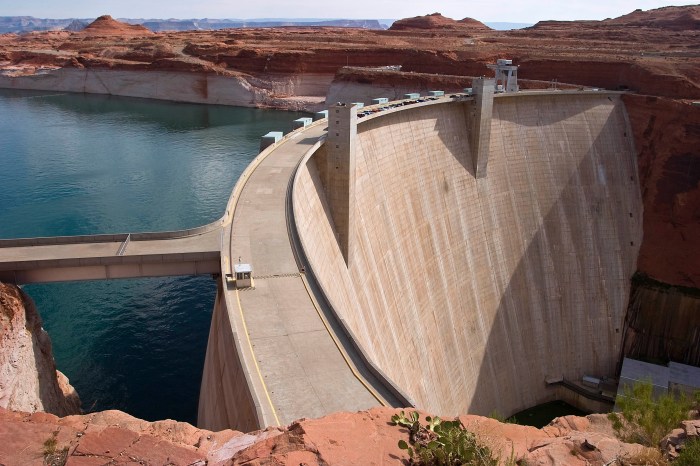

Power-generating dams harness the energy of flowing water to produce electricity. Globally, they contribute a significant portion to the world’s energy supply, with an estimated installed capacity of over 1,300 gigawatts (GW). The energy generation capacity of a dam is primarily determined by its size, water flow rate, and technological advancements.
Larger dams can accommodate greater water volumes and generate more electricity. The water flow rate, influenced by factors such as rainfall patterns and reservoir storage, also impacts energy production. Advancements in turbine technology, such as improved blade designs and materials, have led to increased efficiency and power output.
The geographical distribution of power-generating dams varies widely. China, the United States, and Brazil are among the leading countries in terms of installed capacity. Dams in these regions play a crucial role in meeting their respective energy demands.
Efficiency and Optimization

Energy efficiency in the context of power-generating dams refers to the ratio of electrical energy produced to the total energy input (water flow). Several innovative technologies and practices have been implemented to enhance dam efficiency.
- Adjustable turbine blades: Allow for optimization of water flow and power generation based on varying conditions.
- Advanced control systems: Monitor and regulate dam operations to maximize efficiency and minimize losses.
- Improved spillway designs: Reduce energy dissipation during periods of excess water flow.
Regular maintenance and monitoring are essential for optimizing energy production. By addressing potential issues promptly, such as sediment accumulation or equipment wear, dams can operate at optimal efficiency levels.
Environmental Impact
Power-generating dams can have significant environmental implications, primarily due to the alteration of water flow patterns and habitats. The construction of dams can disrupt fish migration, alter downstream water temperatures, and impact riparian ecosystems.
To mitigate these impacts, various measures are taken, including:
- Fish ladders and bypass channels: Allow fish to migrate around dams.
- Environmental flow releases: Maintain downstream water flows to support aquatic ecosystems.
- Habitat restoration: Create or enhance habitats to compensate for lost or altered areas.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, offer potential alternatives or complements to power-generating dams, with reduced environmental impact.
Economic Considerations
Power-generating dams provide significant economic benefits, including job creation during construction and operation, and infrastructure development for surrounding communities.
However, the construction and maintenance of dams can also involve substantial costs. These include:
- Materials and labor for dam construction.
- Land acquisition and resettlement costs.
- Ongoing operation and maintenance expenses.
The economic viability of power-generating dams compared to other energy sources depends on factors such as construction costs, energy production potential, and environmental regulations.
Case Studies and Examples

The Three Gorges Dam in China is the world’s largest hydroelectric power plant, with an installed capacity of 22.5 GW. Its construction involved the relocation of over 1 million people and the creation of a massive reservoir.
The Itaipu Dam, located on the border of Brazil and Paraguay, is another notable example. With a capacity of 14 GW, it generates a significant portion of electricity for both countries.
The Hoover Dam in the United States, while not primarily intended for power generation, also contributes to electricity production and has played a vital role in flood control and water storage.
Future Trends and Developments: The Amount Of Energy Produced By Power-generating Dams Is
Emerging trends in power-generating dams include:
- Increased focus on efficiency and environmental sustainability.
- Integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels on dam structures.
- Advanced monitoring and control systems to optimize dam operations.
These developments aim to enhance the sustainability and economic viability of power-generating dams while minimizing their environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors influence the energy production capacity of power-generating dams?
The energy production capacity of power-generating dams is influenced by several factors, including dam size, water flow, and technological advancements.
How do power-generating dams contribute to regional energy production?
Power-generating dams play a significant role in regional energy production, providing a reliable and renewable source of electricity to communities and industries.
What measures are taken to mitigate the environmental impacts of power-generating dams?
To mitigate the environmental impacts of power-generating dams, measures such as fish passageways, habitat restoration, and water flow management are implemented.