Pal histology lymphatic system lab practical question 1 – PAL Histology: Lymphatic System – Lab Practical Question 1 provides a comprehensive exploration of the lymphatic system’s histological features, equipping you with the knowledge to analyze tissue samples and identify lymphatic vessels and tissues.
Delving into the intricate structure and function of lymphatic vessels and tissues, this guide unravels the organization and composition of lymph nodes, tonsils, and the spleen, empowering you to confidently navigate the complexities of the lymphatic system.
Microscopic Histology of the Lymphatic System
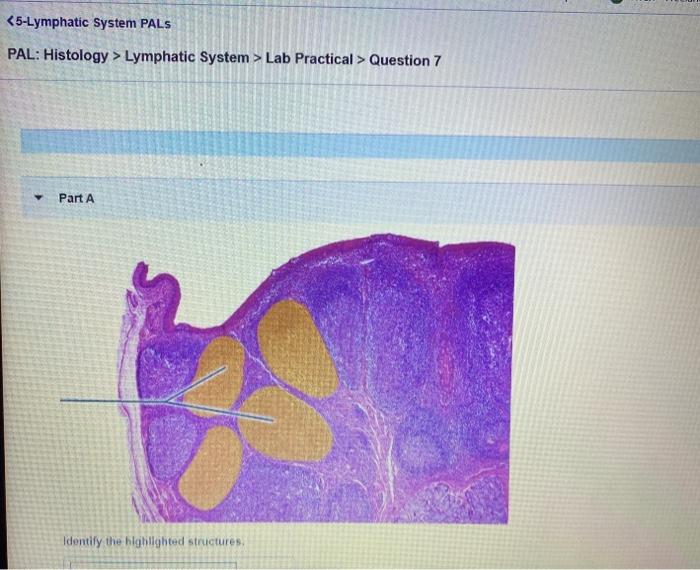
The lymphatic system is a complex network of vessels and tissues that plays a crucial role in the body’s immune response and fluid balance. Histologically, the lymphatic system exhibits unique features that distinguish it from other organ systems.
Structure and Function of Lymphatic Vessels
- Lymphatic capillaries: The smallest lymphatic vessels, responsible for the initial uptake of fluid and antigens from tissues.
- Collecting vessels: Larger vessels that collect lymph from capillaries and transport it to lymph nodes.
- Lymphatic ducts: Major vessels that drain lymph from lymph nodes and return it to the bloodstream.
Organization and Composition of Lymphatic Tissues
- Lymph nodes: Small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph and contain immune cells, including lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells.
- Tonsils: Collections of lymphatic tissue located in the pharynx and nasopharynx, providing a first line of defense against pathogens.
- Spleen: A large organ located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen, involved in filtering blood, removing old red blood cells, and producing lymphocytes.
Practical Question 1: Pal Histology Lymphatic System Lab Practical Question 1
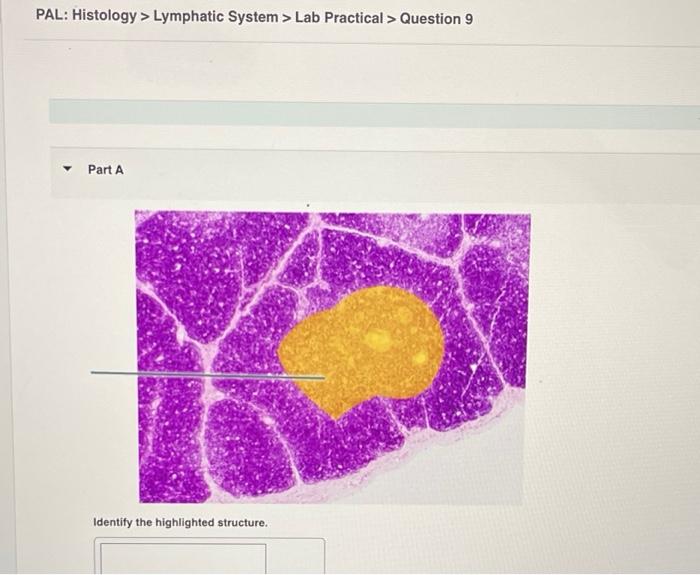
Analyze the provided tissue sample and identify the lymphatic vessels and tissues present.
Morphological Characteristics of Lymphatic Vessels
- Thin walls with a single layer of endothelial cells.
- Absence of a muscular layer or valves.
- Irregular lumen with overlapping endothelial cells.
Histological Features of Lymphatic Tissues
- Presence of lymphocytes, macrophages, and reticular fibers.
- Germinal centers in lymph nodes, containing B cells and follicular dendritic cells.
- Red pulp in the spleen, containing macrophages and red blood cells.
Differential Diagnosis
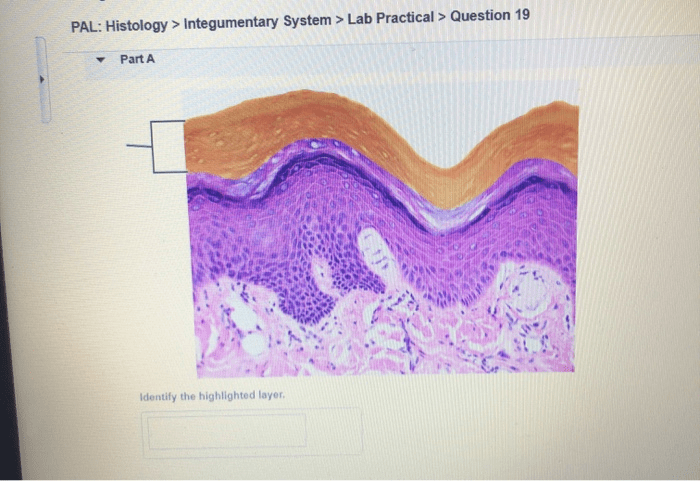
Distinguishing lymphatic vessels and tissues from other structures in the body is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Lymphatic Vessels vs. Blood Vessels, Pal histology lymphatic system lab practical question 1
- Lymphatic vessels have thinner walls and lack a muscular layer.
- Lymphatic vessels have an irregular lumen, while blood vessels have a circular lumen.
Lymphatic Tissues vs. Connective Tissue
- Lymphatic tissues contain lymphocytes and macrophages, while connective tissue does not.
- Lymphatic tissues have a reticular network of fibers, while connective tissue has a collagenous or elastic network.
Clinical Significance
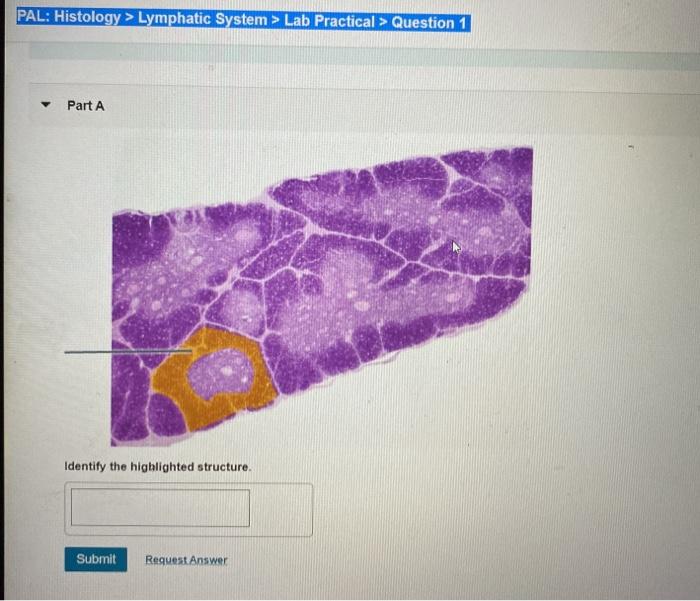
Histological examination of the lymphatic system aids in the diagnosis and management of lymphatic disorders.
Lymphedema
A condition characterized by abnormal accumulation of fluid in tissues, often due to impaired lymphatic drainage.
Lymphoma
A group of cancers that originate in the lymphatic system, characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of lymphocytes.
FAQ Explained
What are the key histological features of lymphatic vessels?
Lymphatic vessels are characterized by their thin walls, irregular lumen, and the presence of valves.
How can you distinguish between lymphatic vessels and blood vessels?
Lymphatic vessels have a thinner wall, lack red blood cells, and have a more irregular lumen compared to blood vessels.
What is the role of lymphocytes in the lymphatic system?
Lymphocytes are responsible for the immune response and are found in high concentrations in lymphatic tissues.