Give the iupac name of the following compounds – Delving into the realm of organic chemistry, the systematic nomenclature of compounds plays a pivotal role in identifying and classifying these intricate molecules. This guide embarks on a comprehensive exploration of IUPAC nomenclature, providing a structured framework for assigning unique and meaningful names to organic compounds.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established a set of guidelines that govern the naming of organic compounds, ensuring consistency and clarity in scientific communication. These rules encompass the identification of functional groups, determination of the parent chain, and the incorporation of substituents, ultimately leading to the derivation of the IUPAC name.
IUPAC Nomenclature

IUPAC nomenclature is a set of rules for naming organic compounds. These rules are established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and are used by chemists around the world to ensure that organic compounds are named in a consistent and unambiguous manner.
Principles and Guidelines
- The name of an organic compound is based on its structure.
- The parent chain is the longest carbon chain in the molecule.
- The substituents are the groups of atoms that are attached to the parent chain.
- The name of the compound is derived from the name of the parent chain and the names of the substituents.
Functional Groups
Functional groups are groups of atoms that have characteristic chemical properties. The presence of a functional group in a molecule determines the chemical reactivity of the molecule.
Nomenclature Rules
- The name of a functional group is based on its structure.
- The name of a compound is derived from the name of the functional group and the name of the parent chain.
Parent Chain
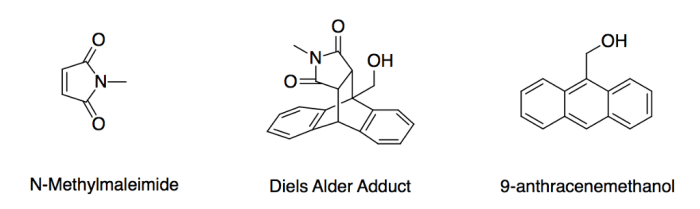
The parent chain is the longest carbon chain in the molecule. The parent chain is used to determine the name of the compound.
Guidelines for Determining the Longest Carbon Chain, Give the iupac name of the following compounds
- The carbon chain must be continuous.
- The carbon chain must have the maximum number of carbon atoms.
- The carbon chain must have the maximum number of double bonds and triple bonds.
Substituents
Substituents are the groups of atoms that are attached to the parent chain. Substituents can be classified as alkyl groups, alkenyl groups, alkynyl groups, or aryl groups.
Rules for Naming and Numbering Substituents
- The name of a substituent is based on its structure.
- The substituent is numbered according to its position on the parent chain.
- The number of the substituent is placed before the name of the substituent.
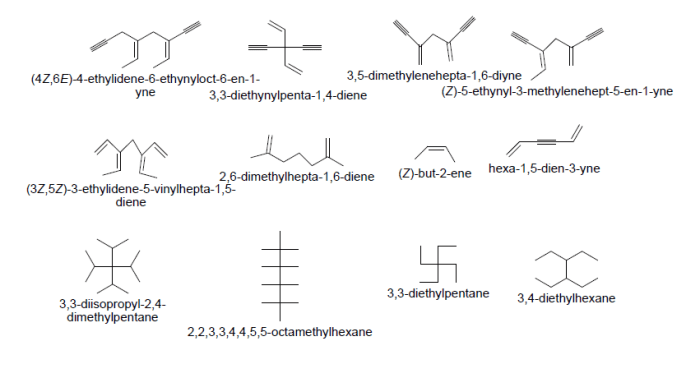
Examples and Exercises
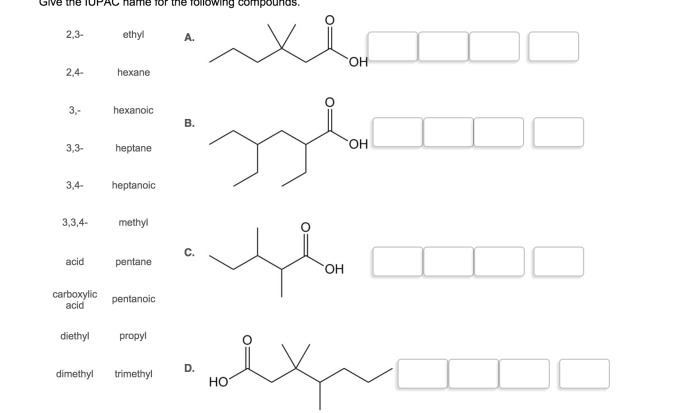
Table of Examples
| Compound | IUPAC Name |
|---|---|
| CH3CH2OH | Ethanol |
| CH3CH2CH2COOH | Butanoic acid |
| CH3CH2CH=CH2 | 1-Butene |
Practice Exercises
- Name the following compound: CH3CH 2CH(CH 3)CH 2CH 3
- Draw the structure of the following compound: 2-methyl-3-hexanone
Advanced Topics
Nomenclature of Polycyclic Compounds
Polycyclic compounds are compounds that contain two or more rings. The nomenclature of polycyclic compounds is more complex than the nomenclature of acyclic compounds.
Nomenclature of Heterocyclic Compounds
Heterocyclic compounds are compounds that contain one or more rings that contain atoms other than carbon. The nomenclature of heterocyclic compounds is more complex than the nomenclature of carbocyclic compounds.
Nomenclature of Coordination Complexes
Coordination complexes are compounds that contain a metal ion that is bonded to a group of ligands. The nomenclature of coordination complexes is more complex than the nomenclature of organic compounds.
Expert Answers: Give The Iupac Name Of The Following Compounds
What is the significance of IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature provides a standardized and universally recognized system for naming organic compounds, ensuring clarity and consistency in scientific communication and research.
How are functional groups identified in IUPAC nomenclature?
Functional groups are identified based on their characteristic chemical structures and properties. IUPAC nomenclature assigns specific prefixes or suffixes to indicate the presence of different functional groups.
What is the role of the parent chain in IUPAC nomenclature?
The parent chain represents the longest continuous carbon chain in the molecule. It serves as the foundation for determining the base name of the compound.