Uniform circular motion gizmo answers – Delving into the realm of uniform circular motion, this guide unveils the answers to the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo, an invaluable tool for exploring the intricacies of this fundamental concept. Through a comprehensive overview, we will unravel the purpose, functionality, and applications of this gizmo, empowering you with a deep understanding of uniform circular motion.
As we embark on this journey, we will delve into the variables and parameters that shape the motion of objects in uniform circular paths. By manipulating these parameters, we will uncover the factors that influence velocity, acceleration, and centripetal force.
Furthermore, we will guide you in collecting and analyzing data from the gizmo, equipping you with the skills to interpret and draw meaningful conclusions from your observations.
Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo Overview: Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo Answers
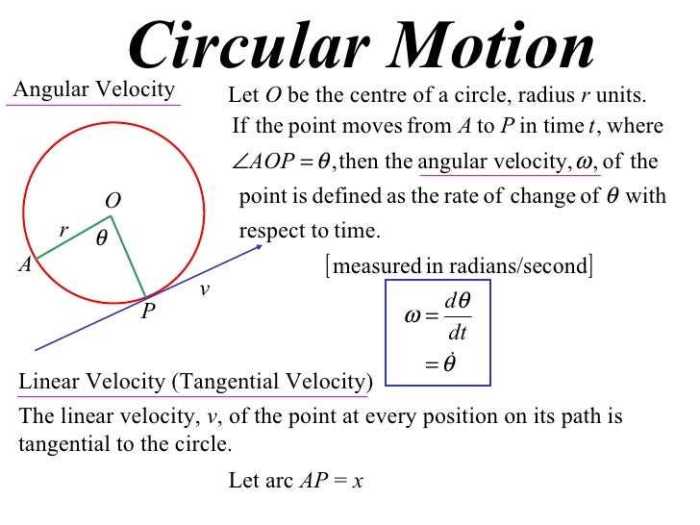
The Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo is an interactive simulation that allows users to explore the concepts of uniform circular motion. The gizmo features a rotating object that can be manipulated by changing its velocity, radius, and mass. Users can collect data on the object’s motion and analyze it to determine its centripetal acceleration, period, and frequency.
The gizmo is a valuable tool for students learning about uniform circular motion. It provides a visual representation of the concepts and allows users to experiment with different variables to see how they affect the object’s motion.
Variables and Parameters, Uniform circular motion gizmo answers
The Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo allows users to manipulate several variables and parameters that affect the object’s motion. These include:
- Velocity:The velocity of the object can be changed by dragging the slider or entering a value in the text box. Velocity is measured in meters per second (m/s).
- Radius:The radius of the circle can be changed by dragging the slider or entering a value in the text box. Radius is measured in meters (m).
- Mass:The mass of the object can be changed by dragging the slider or entering a value in the text box. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg).
These variables and parameters can be used to explore the relationship between velocity, radius, mass, centripetal acceleration, period, and frequency.
Data Collection and Analysis
The Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo allows users to collect data on the object’s motion. This data can be used to determine the object’s centripetal acceleration, period, and frequency.
To collect data, users can click the “Start” button. The gizmo will then record the object’s position, velocity, and acceleration at regular intervals. This data can be viewed in the “Data” table.
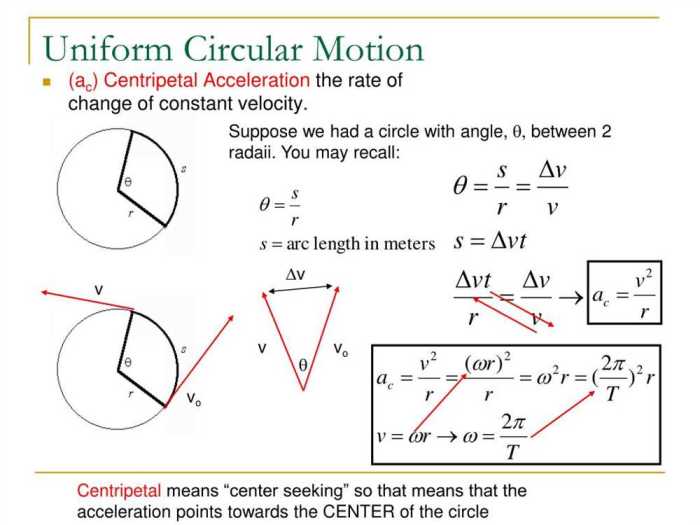
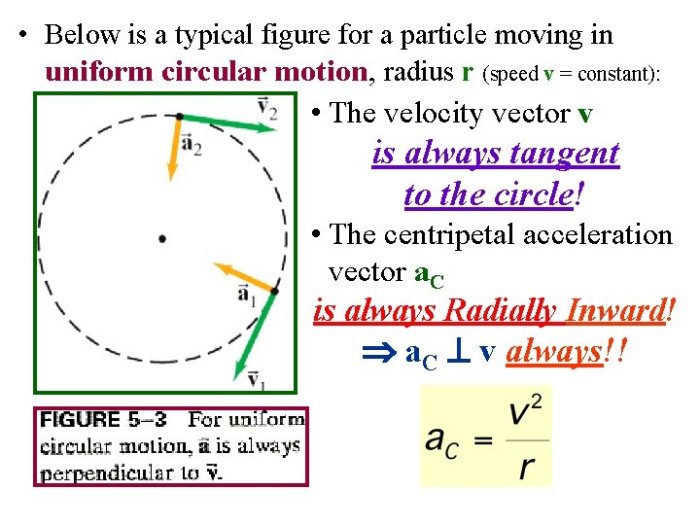
Once the data has been collected, users can analyze it to determine the object’s centripetal acceleration, period, and frequency. The centripetal acceleration can be calculated using the following formula:
ac= v 2/r
where:
- a cis the centripetal acceleration in meters per second squared (m/s 2)
- v is the velocity in meters per second (m/s)
- r is the radius in meters (m)
The period can be calculated by measuring the time it takes for the object to complete one revolution. The frequency can be calculated by dividing 1 by the period.
Real-World Applications
Uniform circular motion is a common phenomenon in the real world. It is found in many applications, such as:
- Rotating machinery:Uniform circular motion is used in rotating machinery, such as engines, turbines, and generators.
- Transportation:Uniform circular motion is used in transportation, such as cars, airplanes, and trains.
- Sports:Uniform circular motion is used in sports, such as baseball, basketball, and tennis.
Understanding uniform circular motion is important for engineers, scientists, and anyone else who works with rotating machinery or objects in motion.
Extensions and Activities
The Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo can be used to explore a variety of extensions and activities. These include:
- Investigating the relationship between velocity, radius, and centripetal acceleration:Users can use the gizmo to investigate the relationship between velocity, radius, and centripetal acceleration. They can change the velocity and radius of the object and observe how these changes affect the centripetal acceleration.
- Designing a roller coaster:Users can use the gizmo to design a roller coaster. They can change the velocity, radius, and mass of the roller coaster and observe how these changes affect the centripetal acceleration and period of the roller coaster.
- Building a model of a planet’s orbit:Users can use the gizmo to build a model of a planet’s orbit. They can change the velocity and radius of the planet and observe how these changes affect the period of the planet’s orbit.
These are just a few examples of the many extensions and activities that can be used with the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo.
Questions Often Asked
What is the purpose of the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo?
The Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo is designed to provide an interactive and engaging environment for exploring the concepts of uniform circular motion. It allows users to manipulate variables such as velocity, radius, and mass to observe how these factors affect the motion of an object moving in a circular path.
How do I collect data from the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo?
To collect data from the Uniform Circular Motion Gizmo, simply run the simulation and record the values of the desired variables at specific time intervals. The gizmo provides real-time data on velocity, acceleration, centripetal force, and other relevant parameters.
What are some real-world applications of uniform circular motion?
Uniform circular motion has numerous real-world applications, including the motion of satellites in orbit, the rotation of amusement park rides, and the operation of washing machines and dryers. Understanding uniform circular motion is essential for engineers, physicists, and anyone interested in the dynamics of rotating objects.