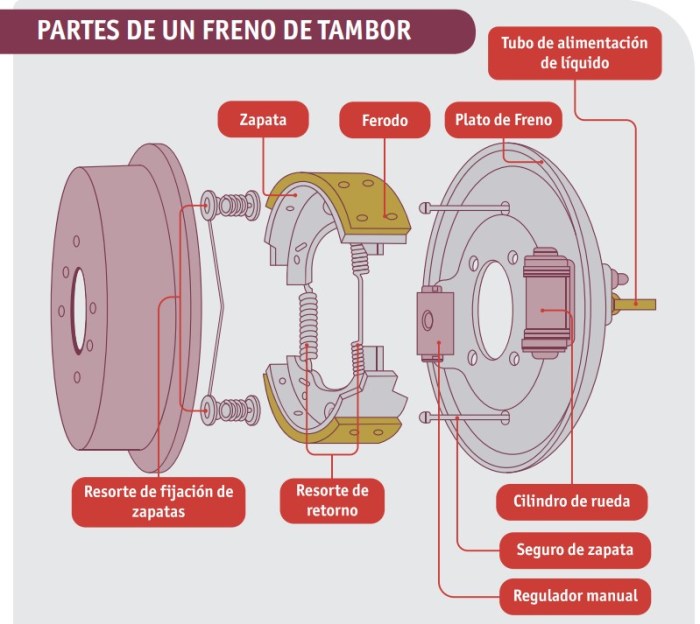
El diagrama de frenos de tambor nos adentra en un fascinante viaje de ingeniería, donde descubriremos los intrincados mecanismos que hacen posible detener un vehículo de manera segura. Esta guía integral proporciona una descripción detallada de los componentes, el funcionamiento y el mantenimiento de los frenos de tambor, ofreciéndonos una valiosa comprensión de un aspecto crucial de la seguridad automotriz.
Los frenos de tambor, con su diseño simple pero eficaz, han sido un pilar de los sistemas de frenado durante décadas. A medida que nos adentramos en este diagrama, desentrañaremos los secretos de su funcionamiento, exploraremos los diferentes tipos y aprenderemos las mejores prácticas para su mantenimiento y resolución de problemas.
Overview of Drum Brake Diagram: Diagrama De Frenos De Tambor
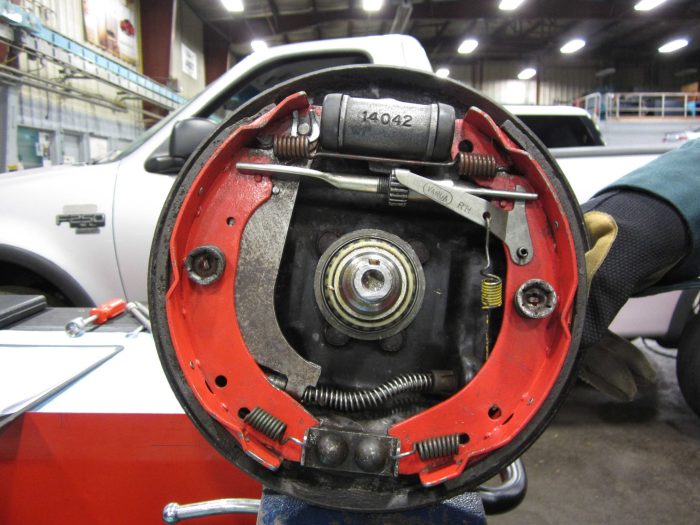

Drum brakes are a type of braking system commonly used in automobiles and other vehicles. They consist of a cylindrical brake drum that rotates with the wheel and a set of brake shoes that press against the inner surface of the drum to slow down or stop the wheel.
Main Components
The main components of a drum brake assembly include:
- Brake Drum:A cylindrical metal component that rotates with the wheel and provides a friction surface for the brake shoes.
- Brake Shoes:Curved, lining-covered components that press against the inner surface of the brake drum to generate friction and slow down the wheel.
- Actuating Mechanism:A mechanical or hydraulic system that applies force to the brake shoes, causing them to press against the brake drum.
Components of Drum Brake Diagram
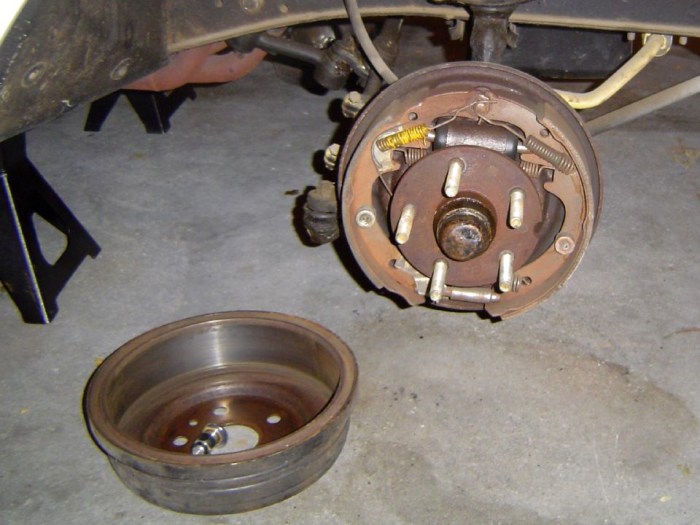

Drum brake systems consist of various components working together to slow down or stop a vehicle. The primary elements include the brake drum, brake shoes, and actuating mechanism.
Brake Drum
The brake drum is a cylindrical metal component that rotates with the wheel. Its inner surface is designed with a specific friction material to create friction against the brake shoes.
Brake Shoes, Diagrama de frenos de tambor
Brake shoes are curved, shoe-shaped components lined with friction material. They are positioned inside the brake drum and are designed to make contact with the inner surface of the drum when actuated.
Actuating Mechanism
The actuating mechanism is responsible for engaging the brake shoes against the brake drum. It typically consists of a hydraulic or mechanical system that applies force to the brake shoes, causing them to press against the drum and generate friction.
Working Principle of Drum Brake Diagram

The working principle of a drum brake diagram involves a series of events that occur when the brake pedal is depressed. These events lead to the generation of friction and the resulting braking effect.
When the brake pedal is depressed, the actuating mechanism, typically a hydraulic system, transmits force to the brake shoes. The brake shoes are then forced against the inner surface of the brake drum, which is attached to the wheel.
Generation of Friction
As the brake shoes come into contact with the brake drum, friction is generated between the two surfaces. This friction creates a resistance to the rotation of the brake drum, which in turn slows down the rotation of the wheel.
The amount of friction generated is directly proportional to the force applied to the brake shoes and the coefficient of friction between the two surfaces. The coefficient of friction is a measure of the resistance to sliding between two surfaces.
Braking Effect
The friction generated between the brake shoes and the brake drum creates a braking effect, which slows down the rotation of the wheel. This braking effect is proportional to the amount of friction generated.
The braking effect of a drum brake diagram can be increased by increasing the force applied to the brake shoes or by increasing the coefficient of friction between the two surfaces.
Types of Drum Brake Diagrams
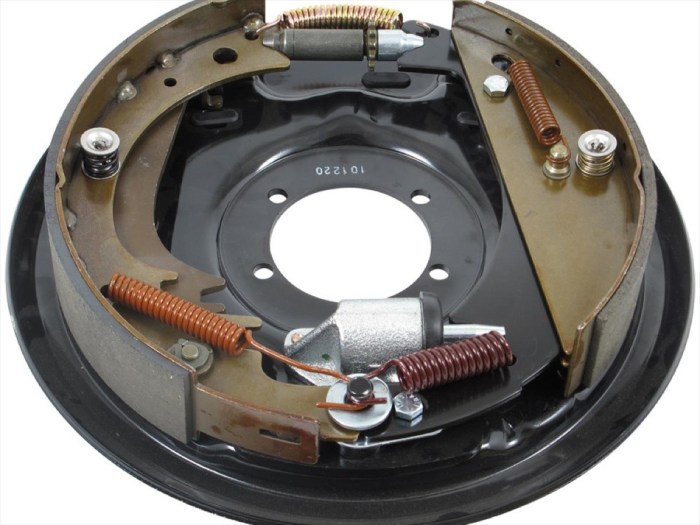

Drum brake designs vary in terms of the arrangement of the brake shoes and the actuation mechanism. The two main types of drum brake diagrams are single-leading shoe systems and double-leading shoe systems.
Single-Leading Shoe Systems
In single-leading shoe systems, one brake shoe is fixed while the other is movable. The fixed shoe is anchored to the backing plate, while the movable shoe is actuated by a hydraulic or mechanical force. When the brake pedal is depressed, the movable shoe pivots on a fixed point and presses against the inner surface of the brake drum, creating friction that slows down the wheel.
Single-leading shoe systems are simpler in design and easier to manufacture compared to double-leading shoe systems. However, they have a tendency to generate uneven brake wear, as the fixed shoe does not move and therefore does not contribute to the braking action.
Double-Leading Shoe Systems
In double-leading shoe systems, both brake shoes are movable and are actuated by a hydraulic or mechanical force. When the brake pedal is depressed, both shoes pivot on their fixed points and press against the inner surface of the brake drum, creating friction that slows down the wheel.
Diagrama de frenos de tambor, yang merupakan komponen penting dalam sistem pengereman, berfungsi dengan cara yang unik. Mekanisme ini bergantung pada gesekan yang dihasilkan antara kampas rem dan permukaan drum yang berputar. Gesekan ini menciptakan gaya pengereman yang memperlambat atau menghentikan kendaraan.
Menariknya, prinsip yang sama juga berlaku pada ir spectrum of 2 butanol , di mana gugus fungsi yang berbeda menghasilkan serapan pada panjang gelombang tertentu, memberikan informasi berharga tentang struktur molekul. Kembali ke diagrama de frenos de tambor, memahami prinsip kerjanya sangat penting untuk memastikan sistem pengereman yang efisien dan aman.
Double-leading shoe systems provide more even brake wear compared to single-leading shoe systems, as both shoes move and contribute to the braking action. However, they are more complex in design and more difficult to manufacture.
The following table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of single-leading shoe systems and double-leading shoe systems:
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Leading Shoe Systems | – Simpler in design- Easier to manufacture | – Uneven brake wear |
| Double-Leading Shoe Systems | – More even brake wear | – More complex in design- More difficult to manufacture |
Applications
Single-leading shoe systems are commonly used in low-performance vehicles, such as small cars and motorcycles. Double-leading shoe systems are commonly used in high-performance vehicles, such as sports cars and race cars.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Drum Brakes
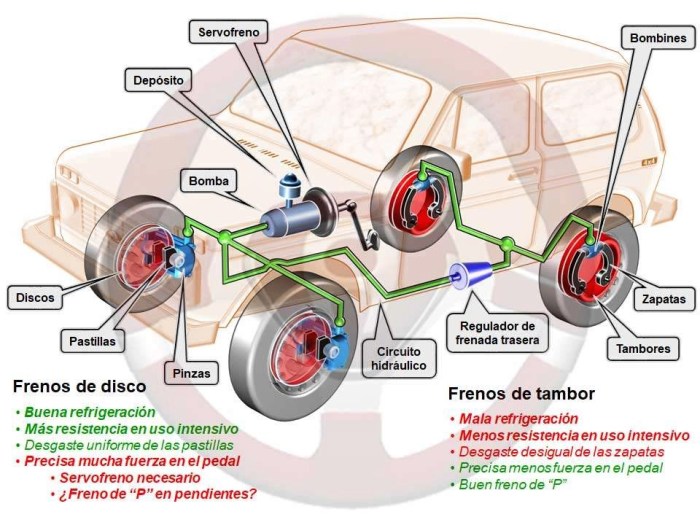
Regular maintenance is crucial for the optimal performance and safety of drum brakes. Neglecting maintenance can lead to premature wear, reduced braking efficiency, and potential safety hazards.
Inspection and Replacement of Brake Shoes
Inspecting and replacing brake shoes is a key part of drum brake maintenance. Worn brake shoes can compromise braking performance and cause uneven wear on the brake drums. Here’s a step-by-step guide for inspecting and replacing brake shoes:
- Remove the wheel and brake drum.
- Check the brake shoes for wear. Replace them if they are worn beyond the recommended thickness or if they show signs of uneven wear.
- Clean the brake drums and backing plates with a brake cleaner.
- Install the new brake shoes, ensuring they are properly aligned and adjusted.
- Reinstall the brake drum and wheel.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues with drum brakes include brake fade and uneven wear. Here are some troubleshooting techniques to address these issues:
Brake Fade
Brake fade occurs when the brakes lose effectiveness due to excessive heat buildup. This can be caused by heavy braking or prolonged use in hilly areas. To address brake fade:
- Allow the brakes to cool down by driving at a slow speed for a short period.
- Check the brake fluid level and top up if necessary.
- Inspect the brake pads for wear and replace if needed.
Uneven Wear
Uneven wear on brake shoes can cause poor braking performance and premature failure. This can be caused by misaligned brake shoes or a worn brake drum. To address uneven wear:
- Inspect the brake shoes and brake drum for wear or damage.
- Adjust the brake shoes to ensure even contact with the brake drum.
- Replace worn brake shoes or a damaged brake drum.
Regular maintenance and timely troubleshooting can help extend the lifespan of drum brakes and ensure their optimal performance.
FAQ
¿Cuáles son los principales componentes de un freno de tambor?
Los componentes principales incluyen el tambor de freno, las zapatas de freno y el mecanismo de accionamiento.
¿Cómo funcionan los frenos de tambor?
Cuando se pisa el pedal de freno, el mecanismo de accionamiento empuja las zapatas de freno contra el tambor de freno, creando fricción y deteniendo el vehículo.
¿Cuáles son los diferentes tipos de frenos de tambor?
Existen frenos de tambor de zapata simple y de zapata doble, cada uno con sus ventajas y desventajas.